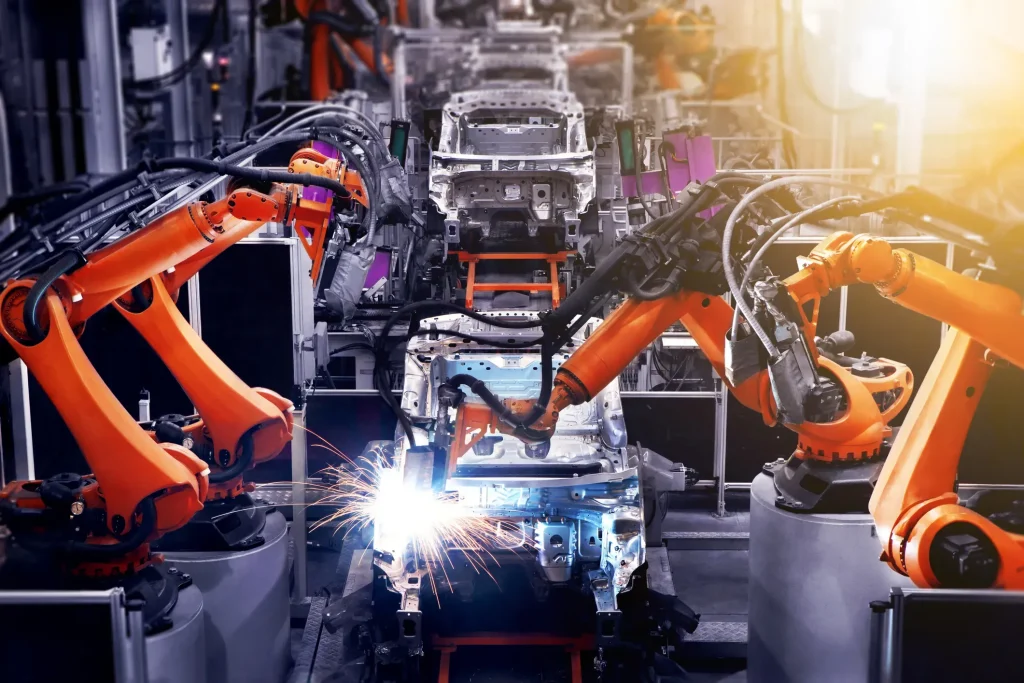
Robotics and Automation in Manufacturing are reshaping how products come to market, how quality is ensured, and how work is distributed across human and machine teams. By adopting industrial robotics, sensors, and smart control software, manufacturers build flexible, high-throughput lines that respond to demand shifts while improving consistency and safety. Automation has moved beyond fixed rigs to modular cells, AGVs, and cobots, expanding capability without sacrificing safety. Leveraging smart factories and AI-trained analytics, plants gain visibility, predictive maintenance, and better product quality across complex, multi-product runs. The result is a scalable, resilient production network where humans and machines collaborate to optimize cost, speed, and safety in modern supply chains.
Viewed through the lens of connected production, the transformation reflects intelligent automation driven by robotic systems, sensors, and data platforms. Instead of isolated machines, firms are deploying modular automation ecosystems that optimize material flow, minimize downtime, and boost traceability. The digitalization of manufacturing, the rise of smart manufacturing environments, and the use of digital twins enable scenario testing and rapid deployment with minimal disruption. Collaborative robots, autonomous mobile robots, and automated guided vehicles work within a unified network to improve throughput while safeguarding workers. In essence, the modern factory becomes a data-driven, adaptive ecosystem that aligns people, processes, and technology for resilient performance.
Robotics and Automation in Manufacturing: Accelerating Smart Factories and Collaborative Robots
Robotics and Automation in Manufacturing are reshaping product development, quality control, and labor distribution by weaving together industrial robotics, automation in manufacturing, and data-driven insights. In modern plants, smart factories rely on collaborative robots sharing space with human operators, enabling flexible lines that adapt to demand shifts without costly reconfiguration. By leveraging AI in manufacturing for sensing, decision-making, and condition monitoring, these systems accelerate throughput while maintaining safety and traceability across the production lifecycle.
Beyond individual machines, the true value comes from orchestrating robots, sensors, software, and analytics to form an end-to-end automation ecosystem. Digital twins simulate processes before they run, predictive maintenance reduces unplanned downtime, and computer vision detects defects early, feeding intelligent controls that adapt in real time. This integrated approach not only boosts quality and throughput but also supports upskilling of the workforce and safer, more engaging jobs.
From Cobots to End-to-End Automation: Realizing Efficiency Across Modern Production
From collaborative robots to fully integrated automation in manufacturing, operations are becoming more resilient through modular robotic cells, intelligent conveyors, and autonomous guided vehicles. The collaboration between humans and machines extends productivity without sacrificing safety, while AI in manufacturing guides scheduling, quality decision-making, and energy management within smart factories.
To maximize ROI and minimize total cost of ownership, organizations adopt a staged deployment—pilot projects, scale-up, and full-scale rollout—paired with robust data governance and cybersecurity. By capturing telemetry from industrial robotics and automation systems, teams can optimize asset utilization, reduce downtime, and ensure traceability and regulatory compliance across product lines.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does automation in manufacturing with industrial robotics and collaborative robots improve throughput and safety in smart factories?
Automation in manufacturing using industrial robotics and collaborative robots (cobots) increases throughput by handling repetitive, dangerous, or high-precision tasks with consistent quality while working alongside people in safe, shared spaces. In smart factories, these systems connect with sensors and software to optimize material flow, routing, and real-time performance monitoring, enabling faster response to demand shifts. Cobots are typically easier to program and cost-effective for high-mix production, supporting scalable automation and safer operations as part of an end-to-end strategy.
How does AI in manufacturing enable robotics and automation in manufacturing within smart factories, and what role do digital twins play?
AI in manufacturing analyzes sensor data to drive predictive maintenance, quality control, and adaptive process control, powering smarter robotics and automation in manufacturing. Digital twins provide a dynamic virtual model of assets and processes, enabling scenario testing, performance optimization, and rapid deployment of new workflows with minimal production disruption in smart factories. Together, AI and digital twins reduce downtime, improve quality, and support continuous improvement across the production lifecycle.
| Aspect | Key Points |
|---|---|
| What Robotics and Automation Do | Reshape product time-to-market, quality, and work distribution across humans and machines; create flexible, resilient systems; integrate robotics, sensors, connectivity, and data analytics. |
| Core Technologies | Industrial robots provide precision, repeatability, and speed for repetitive, dangerous, or high-precision tasks; cobots enable safe collaboration with humans; automation software and sensors connect hardware; modular robotic cells, conveyors, AGVs/AMRs; end-to-end orchestration of hardware, software, and data. |
| AI & Data Analytics | Predictive maintenance; computer vision for detecting defects; AI-driven insights feed control systems for continuous improvement. |
| Digital Twins | Dynamic virtual representations enabling scenario testing, performance optimization, and rapid deployment with minimal disruption; enables smart factories with maximum throughput and safety. |
| Industry Applications | Automotive, electronics, pharma, food & beverage, and logistics use automated systems to boost throughput, precision, cleanliness, traceability, and fast order fulfillment. |
| Implementation Approach | Define a clear value proposition; use phased rollout (pilot, scale-up, full deployment); establish data governance and cybersecurity; design scalable architectures. |
| Workforce & ROI | Upskill workers, create new roles, and provide training in programming, maintenance, and analytics; ROI/TCO includes energy, maintenance, spare parts, software, downtime; automation reduces labor costs and scrap rates and speeds time-to-market. |
| Future & Challenges | Modular, scalable robotic cells; autonomous decision-making; digital twins; safety; cybersecurity; interoperability; change management. |
Summary
Robotics and Automation in Manufacturing is transforming production ecosystems by connecting robots, sensors, data analytics, and intelligent software into an integrated, adaptable manufacturing network. This descriptive overview highlights how end-to-end automation drives throughput, quality, safety, and cost-efficiency across industries, enabling smart factories with real-time visibility, proactive maintenance, and agile responses to demand fluctuations. The convergence supports smarter decision-making, workforce transformation through upskilling, and a path toward sustainable, data-driven operations.