Web development vs software programming shapes how you approach problem-solving, design, and deployment in tech. While both paths share foundational coding skills, they diverge in user experience, system architecture, and the type of problems you solve, with web development offering front-end development, back-end development, or full-stack development tracks. Understanding these distinctions helps you map your career paths in tech and plan a learning trajectory that fits your interests. Key skills include web development essentials like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript for front-end work, plus back-end tools and databases for server-side tasks, while software programming leans on solid fundamentals in languages, data structures, and algorithms. If you’re seeking coding career guidance, these tracks offer clear specialization options and practical steps to get started.
Viewed through an LSI lens, the question can be framed as client-side versus server-side development and the broader practice of software engineering. Other label pairs like frontend development versus backend development, or the umbrella of software development versus desktop and mobile app programming, reflect the same ideas. Using these related terms alongside the core topic helps search engines connect concepts such as career paths in tech and coding career guidance with web development and software programming discussions.
Web development vs software programming: How to decide between browser-focused and system-focused tech paths
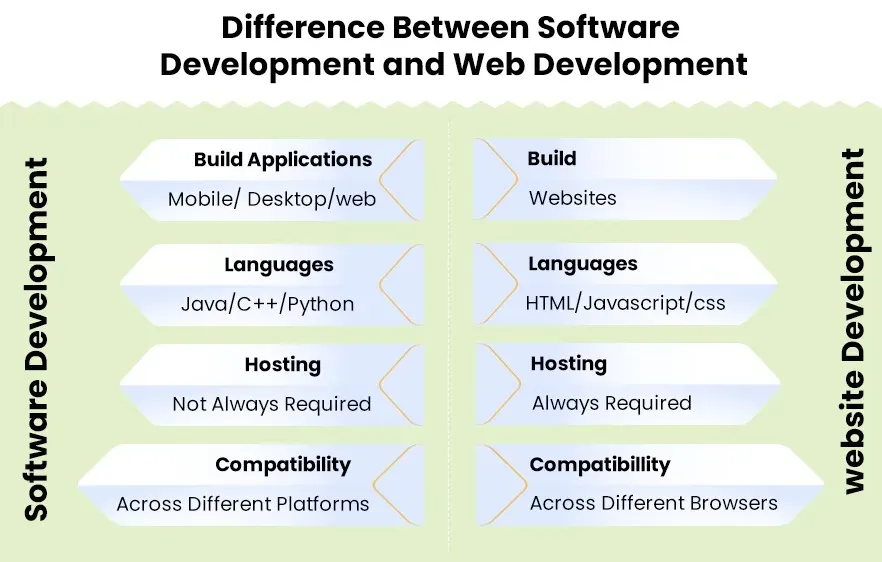
Web development sits at the intersection of design and engineering, delivering browser based experiences through front-end development and back-end development. If you love turning visuals into interactive interfaces, you’ll work with HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and modern front-end libraries like React or Vue, while also wiring up back-end services with Node.js or Python. This path emphasizes the user journey, accessibility, responsive design, performance, and SEO considerations that shape the online experience. A typical web development career may span front-end, back-end, or full-stack development roles, depending on your interests.
Software programming covers a broader landscape beyond the web, including desktop apps, mobile software, embedded systems, and cloud services. It rewards deep problem solving, software design, data structures, algorithms, and robust testing. You may specialize in systems programming, mobile development, game development, or data tooling, and you will use languages such as Java, C++, Python, Go, or Rust, depending on the domain. While many software programmers work on web products, others build core libraries, services, or platforms that operate outside a browser. This path emphasizes architecture, performance, and long-term maintainability.
Career planning in tech: A practical framework for Web development vs software programming
To plan your path, use a practical decision framework that helps you map your interests to concrete outcomes in tech. Define your target outcomes, such as shipping user facing products quickly or building robust software systems used across an organization. Explore sample projects in each path, like a small web app with a rich UI for web development or a modular library that demonstrates architecture for general software programming. Assess the required skills, languages, and tools, then consider how each path aligns with long term career paths in tech, opportunities for specialization, and the kind of coding career guidance you want to pursue.
Take concrete steps today: pick a starter project aligned with your chosen path and complete it end to end, build a portfolio that clearly explains design decisions, contribute to open source to gain experience with real codebases, seek mentorship from professionals in your target field, and practice interview and problem solving relevant to your path, including coding challenges for software programming or system design discussions.
Frequently Asked Questions
Web development vs software programming: How should I choose among front-end development, back-end development, and full-stack development as a career path in tech?
Choosing between Web development vs software programming hinges on whether you prefer building user-facing experiences or solving broader software problems. In Web development, you typically specialize in front-end development (UI/UX with HTML, CSS, JavaScript), back-end development (servers, databases, APIs), or pursue full-stack development (both). Software programming covers a wider domain, including desktop/mobile apps, embedded systems, and tools, with a focus on data structures, algorithms, and software design. Practical steps: explore sample projects in each path, read job descriptions for front-end/back-end/full-stack roles and for software engineering, and seek mentors. Try a few side projects in both domains for a few weeks to see what resonates and aligns with your strengths and interests, which helps with career paths in tech and provides solid coding career guidance.
Web development vs software programming: What skills, learning curves, and job prospects should I expect across web development and broader software programming roles?
Both paths require problem solving and coding, but they emphasize different skill sets. Web development centers on Web development basics—HTML, CSS, JavaScript—and front-end frameworks (e.g., React, Vue, Angular) for user interfaces, plus back-end options (Node.js, Python, Ruby) for server logic if you pursue full-stack. Software programming emphasizes fundamentals like data structures, algorithms, design principles, and language ecosystems (Java, C++, Python, Go, Rust) across domains such as desktop/mobile apps, games, or system software. Job prospects vary by domain: Web development offers clear front-end, back-end, and full-stack tracks with fast feedback and tangible user impact; software programming appeals to those interested in architecture, performance, and cross-domain challenges. For coding career guidance, start with a focused portfolio, practice relevant coding problems, and seek internships or open-source contributions to validate your path.
| Aspect | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Definition/Scope | Web development focuses on building websites and web apps; Software programming covers software beyond the web, such as desktop, mobile, and embedded systems. |
| Core Skills | Web development uses HTML, CSS, JavaScript, frameworks, UX; Software programming emphasizes data structures, algorithms, design, testing, and languages like Java, C++, Python. |
| Technologies | Web development relies on HTML/CSS/JS and web frameworks; back end stacks include Node.js, Django, Rails; Software programming uses domain-specific languages like Java, C++, Go, Rust. |
| User Interaction/Impact | Web development is user-facing in the browser; software programming focuses on architecture, performance, and reliability in diverse environments. |
| Career Tracks | Web development pathways include front-end, back-end, and full-stack; Software programming paths include software engineer, systems programmer, mobile, game, data tooling. |
| Learning Curve | Web development emphasizes design and rapid browser iteration; software programming emphasizes architecture, algorithms, and engineering rigor. |
| Overlap/Convergence | Both require problem solving, version control, debugging, testing, and code quality. Hybrids like full-stack and platform engineering blend skills. |
| Practical Start | Choose a starter project, build a portfolio, contribute to open source, seek mentorship, practice interview problems, decide path. |
| Market Trends | Web continues to grow with online presence and front-end evolution; software programming opportunities in scalable systems, cloud, fintech, healthcare. |
| Education & Skills | Foundational concepts, practical projects, tooling, Git, CI; languages and frameworks aligned to path. |
| Web Specializations | Front-end focuses on UI/UX; Back-end on server logic and data; Full-stack combines both. |
| Software Programming Specializations | Systems programming, mobile apps, game development, data tooling, or tools engineering. |
Summary
Web development vs software programming presents two interconnected paths in tech careers, each with distinct focus areas, skill sets, and opportunities. Web development centers on creating user facing websites and apps with emphasis on usability, accessibility, and responsive interfaces, while software programming spans broader domains such as desktop and mobile apps, embedded systems, and cloud platforms, prioritizing algorithms, data structures, and robust architecture. Your choice depends on whether you prefer tangible interfaces and rapid iteration or deep engineering challenges that cross domains. By trying projects, building a portfolio, and learning core concepts, you can decide which path aligns with your interests and long term goals. A hybrid like full-stack or platform engineering can also offer a blend of both worlds.