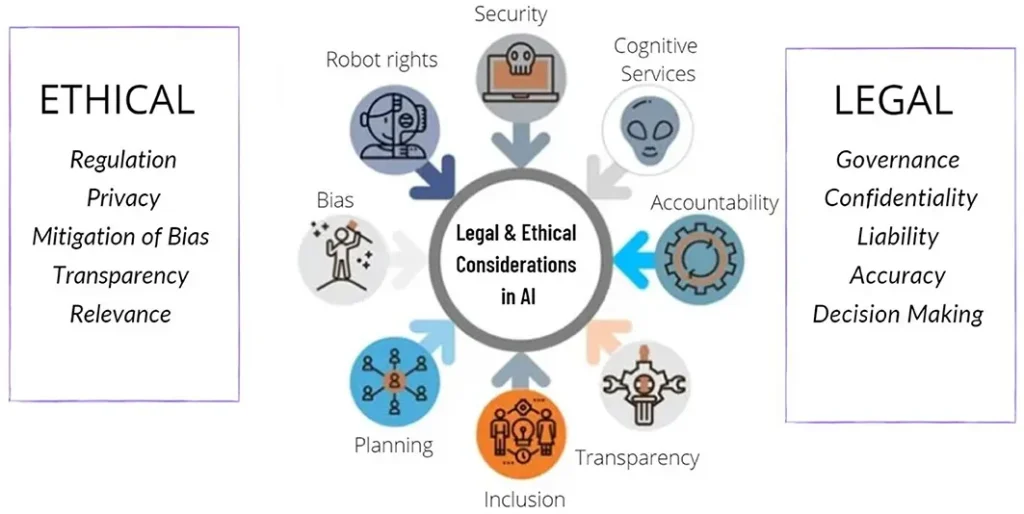
Ethical and Legal Considerations of Rapid Tech Adoption are increasingly central to how organizations innovate, regulators shape policy, and citizens expect responsible use of new capabilities. As technologies accelerate—from artificial intelligence and machine learning to the Internet of Things—the pace of deployment challenges norms around privacy, bias, and accountability, tying into ethical technology adoption. This post outlines practical governance, risk management, and compliance strategies to align rapid deployment with regulatory compliance for emerging technologies. We also address the legal implications of rapid technology deployment, including data protection, liability, and accountability for automated systems. By integrating ethics and compliance into planning and operations, organizations can innovate with confidence while protecting rights and trust.
Beyond the vocabulary of speed, the conversation shifts to accelerated digital transformation and responsible innovation as organizations weave governance into every stage of new tool rollout. Using phrases like rapid technology adoption, emerging tech deployment, and swift digital modernization, teams align strategic aims with privacy, safety, and fairness. LSI-friendly terms such as data governance, accountability frameworks, model risk management, and stakeholder trust help connect ethics, regulation, and technology outcomes. By framing questions around governance structures, due diligence, and continuous monitoring, leaders can navigate cross-border compliance and ethical considerations without stalling progress. In short, strategic planning that emphasizes responsible innovation, transparent decision-making, and proactive risk controls enables sustainable growth in an era of rapid tech change.
Ethical and Legal Considerations of Rapid Tech Adoption: Foundations for Responsible Innovation
Ethical technology adoption should serve as the compass for rapid tech deployment. Organizations must articulate core values and translate them into concrete practices that govern how decisions are made, who is responsible, and how stakeholders are affected. Core principles—transparency, accountability, fairness, and inclusivity—should guide every phase of the technology lifecycle, from data collection and model training to deployment and monitoring. By foregrounding ethical technology adoption, teams can anticipate harms, reduce bias, and preserve human oversight in high-stakes outcomes.
To operationalize these ethics, firms should adopt an ethics-by-design mindset, weaving ethical considerations into product requirements, data governance, and risk assessment from the earliest stages. Building an open culture where concerns can be raised by diverse stakeholders—employees, customers, and affected communities—helps surface potential harms before they escalate. Aligning ethical practices with legal obligations reinforces the idea that responsible innovation is inseparable from governance and accountability, including attention to the legal implications of rapid technology deployment and the need for regulatory compliance for emerging technologies.
Balancing Speed with Accountability: AI Governance, Regulatory Compliance for Emerging Technologies, and Risk Management
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are often at the core of rapid adoption scenarios. AI governance and ethics frameworks provide guardrails to ensure models are fair, explainable where appropriate, and controllable. Establishing governance structures—such as AI ethics boards, model risk management, and clear decision rights about when and how AI is used for high-stakes outcomes—creates accountability and improves trust. Documenting data sources, model choices, and performance metrics supports both ethical standards and legal defensibility.
Effective regulatory compliance for emerging technologies must be embedded in day-to-day operations rather than treated as a separate initiative. Practical steps include privacy-by-design and security-by-design principles, regular impact assessments, auditable decision logs, and rigorous vendor due diligence. A robust risk management approach blends ethics and law into ongoing operations through risk scoring, incident response planning, business continuity, and continuous monitoring of evolving regulations across regions—all aimed at ensuring rapid tech adoption remains aligned with legal requirements and societal norms.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does ethical technology adoption mean in the context of rapid tech deployment, and how does it relate to AI governance and ethics?
Ethical technology adoption means integrating core ethical principles—transparency, accountability, fairness, and inclusivity—into the full lifecycle of rapid technology deployment. It aligns with AI governance and ethics by establishing governance structures (such as AI ethics boards and model risk management), conducting bias audits, ensuring explainability where appropriate, and preserving human oversight for high‑stakes decisions. Practically, it uses ethics‑by‑design, clear decision rights, stakeholder engagement, and ongoing monitoring to balance speed with privacy, safety, and rights protection.
What are the legal implications of rapid technology deployment that organizations should address to ensure regulatory compliance for emerging technologies?
Key legal implications include data privacy and protection laws (e.g., GDPR, CCPA/CPRA), data sovereignty and cross‑border transfers, liability for autonomous systems, IP issues, and sector‑specific regulations. To achieve regulatory compliance for emerging technologies, organizations should implement data minimization and purpose limitation, explicit consent where needed, robust incident response, vendor due diligence, and auditable data flows. They should also embed privacy‑by‑design and security‑by‑design, maintain ongoing monitoring of regulatory changes, and establish clear accountability and contractual terms to define liability and remedies.
| Key Point | Summary |
|---|---|
| 1) Ethics first: building a framework for ethical technology adoption | Establish values and accountability; embrace transparency, fairness, inclusivity; apply ethics-by-design; ensure human oversight and bias screening. |
| 2) Legal foundations: navigating the regulatory landscape for rapid tech deployment | Understand data privacy, protection, liability, IP, and sector-specific rules; implement data minimization, consent where needed, secure handling, and incident response. |
| 3) Regulatory compliance and governance: embedding control mechanisms for emerging tech | Build a living compliance program with data stewardship, privacy/security by design, regular impact assessments, auditable records, and due diligence on vendors. |
| 4) AI governance, ethics, and accountability in rapid tech adoption | Create governance structures, conduct bias audits, ensure explainability where appropriate, and assign clear model performance and remediation responsibilities. |
| 5) Risk management: integrating ethics and law into everyday operations | Perform early risk assessments, score privacy exposure, plan for incident response, and map ethics/legal checks across the technology lifecycle. |
| 6) Case examples: learning from both success and missteps | Illustrative cases (e.g., healthcare AI and loan approvals) show the need to mitigate bias, ensure consent and transparency, allocate liability, and enforce governance. |
| 7) Global and cross-border considerations: harmonizing diverse regimes | Navigate data flows across jurisdictions with universal privacy principles and adaptable governance to meet region-specific rules. |
| 8) Practical steps for organizations: a roadmap to responsible innovation | Define an ethical framework, establish governance and risk controls, design privacy/security by default, perform due diligence on third parties, and maintain ongoing education and stakeholder engagement. |
Summary
Ethical and Legal Considerations of Rapid Tech Adoption guide how organizations balance speed with responsibility, ensuring that innovation serves people, businesses, and the public good. By embedding ethics and legal compliance into governance, risk management, and operations, organizations can accelerate digital transformation while protecting rights and maintaining trust. A proactive approach—transparent decision-making, rigorous governance, data minimization, secure handling, and ongoing stakeholder engagement—helps organizations navigate global and cross-border tech deployment thoughtfully and responsibly.