Version Control and Collaboration for Programmers is the backbone of modern software teams, enabling safe, coordinated changes across dozens of contributors while preserving a clear, searchable history that explains the why behind every decision. This disciplined practice unlocks faster delivery, better traceability, and blameless retrospectives by letting you see who touched which lines and when. Git workflows provide a structured path from local edits to team approvals, helping groups align on when code should be merged, tested, and released. A thoughtful approach to branching strategies reduces merge chaos, clarifies ownership, and makes it easier to isolate work, review changes, and roll back when necessary. With a foundation built on clear processes and good communication, teams can scale collaboration, improve quality, and deliver reliable software on predictable schedules.
Seen from another perspective, source control and repository management are the keystones of collaborative development, enabling teams to protect history while coordinating dozens of edits. These systems share core ideas like change tracking, review, and automated checks that help sustain quality as teams grow and projects scale. In practice, developers work on feature branches, submit pull requests or merge requests, and rely on targeted feedback to refine code. Platforms that offer issue boards, protected branches, and integrated CI/CD reinforce the same principles in an approachable, scalable way. Framing collaboration through history, reviews, and automation clarifies ownership and accelerates learning for new contributors.
Version Control and Collaboration for Programmers: Git Workflows, Branching Strategies, and Code Review Workflows
Version Control and Collaboration for Programmers is more than just saving changes to code; it’s a disciplined practice that unlocks team-wide visibility and coordinated delivery. By embracing Git workflows, teams can structure work around feature branches, release readiness, and robust merge strategies. Branching strategies give teams a map of how work flows, when to ship, and how to parallelize tasks, while code review workflows ensure that every change is examined before joining the main line.
To maximize impact, pair Git workflows with collaboration best practices and version control best practices. Clear review criteria, small, focused pull requests, and timely feedback make code review workflows productive rather than painful. A well-defined branching strategy—whether feature branches, Git Flow, or trunk-based development—helps keep history readable and reduces merge conflicts, supporting a smoother, higher-velocity development process.
Integrating Collaboration Best Practices: Version Control Best Practices, Code Review Workflows, and Continuous Improvement
Solid version control best practices include atomic commits, meaningful messages, consistent hooks, and regular branch pruning. When teams align on these practices, Git workflows become predictable, and collaboration best practices extend from individual contributors to the entire organization. Code review workflows become a learning loop: developers gain feedback, testers verify behavior, and product owners validate outcomes, all within a transparent PR or merge request process.
Beyond tooling, successful collaboration hinges on communication and shared expectations. Document the rationale behind decisions in PR descriptions, define turnaround times for reviews, and automate checks so discussions stay focused on the code rather than process friction. When teams institutionalize these collaboration best practices, the organization can scale release cadence, maintain code quality, and deliver software faster.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the essential Git workflows for Version Control and Collaboration for Programmers, and how do they support collaboration best practices?
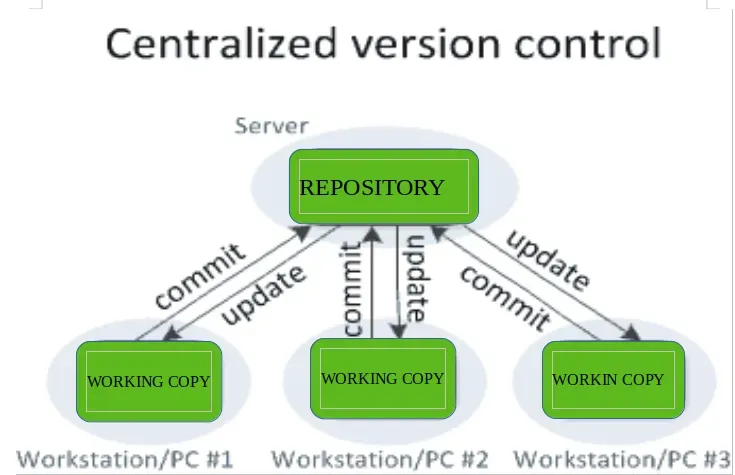
Git workflows provide repeatable patterns for organizing work and merging changes. Common options include centralized workflow, feature-branch workflow, Git Flow, and the forking workflow. Selecting the right workflow supports Version Control and Collaboration for Programmers by reducing merge conflicts, enabling focused code reviews, and aligning with collaboration best practices. Each workflow pairs with a clear pull request/merge request process and automated checks to keep history clean and releases predictable.
How do branching strategies and code review workflows fit into Version Control and Collaboration for Programmers to improve efficiency and quality?
Branching strategies shape how code evolves, with approaches such as feature branching, Git Flow-inspired models, trunk-based development, and release branches. A good strategy improves clarity and stabilizes releases, making reviews smoother. Pair this with code review workflows—clear criteria, timely feedback, small focused changes, and automation hooks—to uphold quality and foster blameless collaboration. Together, they embody Version Control and Collaboration for Programmers and support reliable CI/CD.
| Topic | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Introduction | Version Control and Collaboration for Programmers is at the heart of modern software development. Git enables feature branches, pull requests, and confident merging, forming the collaboration backbone for predictable releases. |
| What Version Control Offers | Preserves history and authorship; enables debugging, blameless retrospectives, and compliance auditing. Benefits include safety net (revert changes), traceability, collaboration, and automation with CI/CD. |
| Git Workflows | Common patterns: Centralized, Feature-branch, Git Flow, and Forking. Selection depends on team size, release cadence, and risk tolerance; aim to minimize merge conflicts and support clear review paths. |
| Branching Strategies | Approaches include Feature branching, Git Flow-inspired, Trunk-based development, and Release branches. Each has trade-offs between review clarity and stability; choose based on project needs and evolve over time. |
| Code Review Workflows | Code reviews improve quality and knowledge sharing. Key practices: clear criteria, timely feedback, small focused changes, automation hooks, and a blameless culture; pull/merge requests provide structured discussion history. |
| Version Control Best Practices | Commit frequently with meaningful messages, make atomic commits, decide when to rebase vs. merge, standardize tooling/hooks, and prune stale branches for long-term stability. |
| Automation and CI/CD | Automation through CI ensures tests run on each change; CD pushes verified changes to production with safeguards like automated rollbacks, reinforcing collaboration across teams. |
| Practical Team Tips | Start with a shared mental model, maintain fast review cycles with small PRs, automate coding standards, document decisions in PRs, and invest in onboarding to accelerate contributor growth. |
| Tools and Platforms | Git-centric platforms like GitHub, GitLab, and Bitbucket provide issue tracking, pull/merge requests, protected branches, and integrated CI/CD to support the chosen workflows and branching strategy. |
| Common Pitfalls | Watch for merge conflicts, inconsistent commit messages, long-lived branches, and sluggish reviews; address with regular merges/rebases, conventional commits, and clear review SLAs. |
| Conclusion (summary points) | With disciplined Version Control and Collaboration for Programmers practices, teams gain reliability, faster delivery, and scalable collaboration. Embracing Git workflows, clear branching, and robust code reviews builds a shared language for changes, reduces risk, and accelerates software delivery. |
Summary
HTML table provides a structured summary of the base content on Version Control and Collaboration for Programmers.