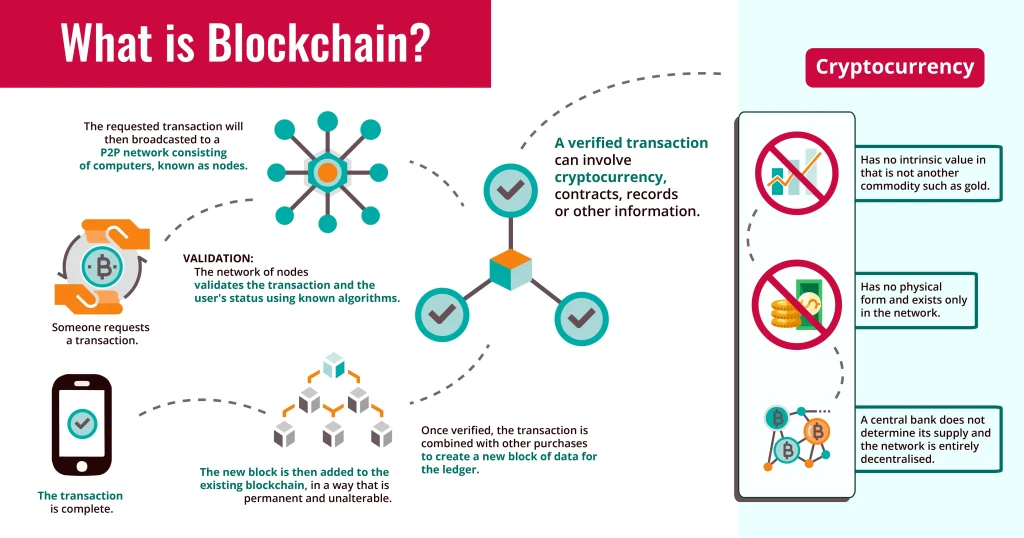
If you’re asking What Is Blockchain?, this guide provides a clear, practical explanation. At its core, the technology is a distributed ledger that records transactions across many computers, making tampering extremely difficult. Unlike centralized databases, blockchain distributes copies of the ledger to a wide network of nodes, which helps ensure transparency, security, and resilience. You’ll hear terms like blockchain basics, all pointing to the same foundational idea. Understanding these elements gives beginners a solid footing to evaluate projects and their real-world use cases.
Beyond the basic definition, it’s often described as a distributed ledger or a tamper-resistant digital notebook that records events across a decentralized network. This framing emphasizes trust built through consensus, cryptographic links, and an auditable history rather than a single central authority. Other LSIs you might encounter include distributed database technology, smart contracts platform, and a public or permissioned ledger that underpins digital money. In practical terms, think of it as a trustworthy log that enables transparent audits, secure transfers, and automated agreements without a central gatekeeper. These alternative terms help beginners connect the idea to real-world uses such as supply chains, identity verification, and governance.
What Is Blockchain? A Beginner’s Guide to Blockchain Technology and How It Works
What is blockchain? In plain terms, a blockchain is a distributed ledger—a digital diary shared across many computers. This design embodies blockchain basics: no single control point, and copies living across the network that help resist tampering. Transactions are grouped into blocks and chained with cryptographic hashes to prior blocks, creating a traceable history that’s difficult to alter.
To understand how blockchain works, imagine a process where a transaction is proposed, broadcast, verified by multiple nodes, packaged into a block, and then confirmed through a consensus mechanism. This decentralized arrangement—the heart of blockchain technology—lets honest participants agree on the current state of the ledger even without a trusted intermediary. Over time, the chain becomes increasingly tamper-evident, since altering past blocks would require re-writing many copies across the network.
From Cryptocurrency Blockchain to Real-World Impact: Practical Uses for Beginners
Beyond crypto, blockchain technology enables real-world uses that benefit from a transparent, tamper-resistant record. In supply chains, every step—from origin to shelf—is logged on a shared ledger, improving traceability and accountability. Digital identity solutions leverage blockchain to give individuals more control over their data while enabling reliable verification by services. For beginners, thinking in terms of ‘cryptocurrency blockchain’ can help connect the technology to tangible examples, but the reach of blockchain technology extends well beyond money.
Smart contracts automate agreements when predefined conditions are met, reducing intermediaries and speeding transactions. Blockchain for beginners should also consider governance models, privacy options, energy use, and scalability. Different networks implement varying consensus mechanisms and access controls, illustrating how ‘blockchain basics’ inform decisions about interoperability, regulation, and practical deployment across industries.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is blockchain? How does blockchain work for beginners?
Blockchain is a distributed ledger kept on many computers (nodes) worldwide. It records transactions in blocks linked by cryptographic hashes, forming an immutable chain with no single central authority; consensus among honest nodes validates updates. In practice, a transaction is proposed, verified by the network, grouped into a block, and added to the chain after consensus. This technology underpins cryptocurrency blockchain but also supports use cases like supply chains, digital identity, and smart contracts—topics you’ll see in blockchain basics, how blockchain works, and blockchain technology discussions for beginners.
What is blockchain technology and how does cryptocurrency blockchain relate to broader uses?
Blockchains are distributed ledgers secured by cryptography and consensus mechanisms. Blockchain technology underpins cryptocurrency blockchain by recording ownership and transfers of digital money without a central bank. Beyond crypto, it enables supply chains, digital identity, and self-executing smart contracts. Core concepts include blocks, hashes, and the previous hash, along with decentralized networks that reduce single points of failure. Different blockchains use different consensus rules and privacy options, affecting scalability and energy use. For beginners, understanding blockchain technology helps you evaluate projects beyond Bitcoin, recognize blockchain for beginners resources, and see how decentralized ledgers may transform various industries.
| Topic | Key Points | Notes / Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Distributed ledger; records transactions across many computers; tamper resistance; no single central authority; blocks linked via cryptographic hashes. | Ledger is shared across network; immutability increases as blocks are added. |
| Key Components | Blocks, Hashes, Previous Hash, Distributed network | Block = data bundle; Hash = data fingerprint; Previous Hash links blocks; Nodes = participants. |
| How It Works (Simple Sequence) | Propose transaction, broadcast, validate, form block, reach consensus, append to chain, share updated state. | Consensus mechanism varies by blockchain. |
| Security & Immutability | Cryptography, Decentralization, Immutability, Consensus mechanisms | Examples include proof of work, proof of stake, etc. |
| Blockchain & Cryptocurrency | Records ownership and transfers; transparent, traceable, secure; underlying tech for digital money | Beyond money, applicable to many other use cases. |
| Real-World Uses | Supply chain transparency, digital identity, smart contracts, voting/governance, data integrity | Provenance, verification, and accountability are common outcomes. |
| Beginner Literacy | Not just Bitcoin; many networks with different rules; privacy vs transparency; energy and scalability trade-offs | Public vs private networks; design trade-offs matter. |
| Getting Started | Guides, explorers, safe practice wallets, learn consensus mechanisms, engage with communities | Hands-on exploration recommended for beginners. |
| Common Misconceptions | Blockchain is not just Bitcoin; it does not automatically solve all problems; adoption needs interoperability and regulation | Clarify scope and real-world limitations. |
Summary
What Is Blockchain? is a foundational technology that enables trust in digital environments without relying on a central intermediary. By recording data in blocks, linking them with cryptographic hashes, and securing the process through decentralized consensus, blockchain creates an auditable history that is difficult to alter. While driven by cryptocurrency in popular imagination, the broader implications of blockchain technology extend to supply chains, identity, governance, and beyond. For newcomers, grasping the basics—the core ideas of what a block, a hash, and a distributed ledger are—provides a solid footing to explore more advanced topics with confidence. As you continue learning, you’ll see why blockchain is widely described as a technology with the potential to transform many sectors, not just finance.